
Hearing loss can present significant challenges, but advancements in technology have led to the development of innovative gadgets designed to improve the quality of life for those affected. From advanced hearing aids to specialized alert systems and smartphone integrations, these devices are tailored to meet the diverse needs of individuals with hearing impairments. Explore some of the best gadgets for hearing that combine functionality, convenience, and cutting-edge technology to empower users in their day-to-day lives.
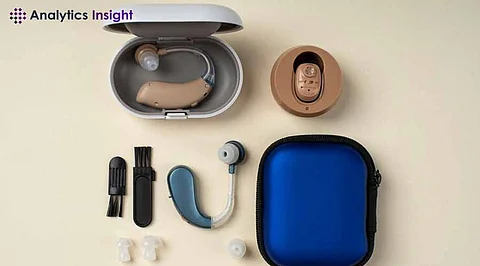
The most common and crucial device for hearing-impaired individuals, hearing aids work by amplifying sound to make speech and other sounds easier to hear and understand.
Modern hearing aids offer features such as digital sound processing, noise reduction, and wireless connectivity, which enables users to listen directly from their smartphones or any other device.
Besides, certain models come with rechargeable batteries, thus cutting down the frequency of battery replacement.
A revolutionary solution exists for individuals with severe to profound hearing loss-in terms of cochlear implants. While hearing aids amplify sound, cochlear implants bypass the damaged parts of the ear and stimulate the auditory nerve directly, allowing for stronger perception of sound.
The external processor and an internal implant are encompassed in these devices, and they require surgical implantation. They are most helpful for those who do not benefit from traditional hearing aids.
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) are designed to improve the signal-to-noise ratio, helping individuals hear desired sounds more effectively in challenging listening environments. This category includes personal amplifiers, FM systems, and loop systems.
Portable sound-amplifying devices, ideal for one-on-one conversations or watching TV, are common ALDs. FM systems use radio signals to send sound directly from a speaker’s microphone to the listener’s hearing aid or cochlear implant, ensuring clear audio transmission. Loop systems, also known as induction loops, transmit sound to telecoil-equipped hearing aids, reducing background noise and enhancing clarity for the user.
The real-time text captions of phone conversations as displayed on captioned telephones make it easier for such people to understand the conversation going on. These phones use voice recognition technology wherein words spoken are converted into text through a screen.
This allows reading as one listens so that one does not miss anything important. Captioned telephones are especially useful for people who are not able to clearly understand speech over the phone.
Traditional alarm clocks can be ineffective for individuals with hearing loss, as the sound may go unheard. Vibrating alarm clocks provide a practical solution by using vibrations to wake the user.
These clocks typically include a vibrating pad that can be placed under a pillow or mattress. When the alarm activates, the pad vibrates to alert the user without relying on sound. Some advanced models also incorporate flashing lights, offering an additional visual cue to ensure a more effective and reliable wake-up system.
Visual alert systems use flashing lights or vibrations to alert people to important sounds in their surroundings, such as doorbells, telephone calls, or smoke alarm signals. These types are crucial and indeed very vital when it comes to safety and alerts, especially in emergencies.
Visual alert systems can be incorporated into any number of household appliances, offering a visual warning for different alerts. For instance, a doorbell alert system may flash some lights indicating the presence of an individual at the door while a smoke alarm alert may incorporate flashing lights and vibrations to get the attention of the user toward the threat.
For individuals with hearing loss, watching TV can be challenging, especially when dialogue isn't clear. TV listening systems enhance the experience by transmitting clear, amplified sound directly to hearing aids or headphones.
These systems utilize technologies such as infrared, FM, or Bluetooth to deliver high-quality audio. Many models also allow users to adjust the volume independently of the TV speakers, ensuring a comfortable listening experience without disrupting others.
A wide range of smartphone applications is available to assist individuals with hearing loss. These apps offer features such as natural sound amplification for various environments, real-time captioning for conversations, monitoring sound levels, managing tinnitus, and adjusting hearing aid settings.
By leveraging smartphone technology, these apps empower users to stay more connected and engaged with their surroundings, significantly enhancing their daily experiences.
Whether it’s hearing aids, cochlear implants, visual alert systems, or smartphone applications, these tools address unique challenges and create opportunities for seamless communication and interaction.
