
Python is a high-level programming language used for a variety of tasks, including creating websites and applications, displaying and analyzing data, and automating tasks. It also imparts excellent knowledge of how to use mathematical, statistical, and scientific operations. Additionally, it provides outstanding libraries for use with data science applications. Python is also preferred among ML scientists in terms of application domains.
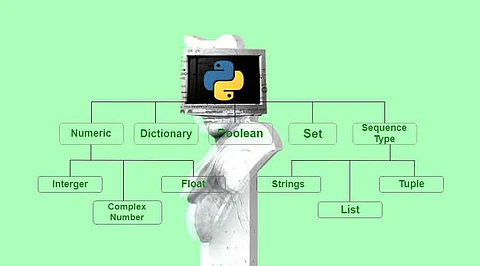
Python offers a variety of data types that let you efficiently store and manipulate data. We'll look at a few of the key Python data types that are frequently used in applications for data science in this article.
Python supports various numeric data types, including integers (int) and floating-point numbers (float). Integers are whole numbers, while floating-point numbers can have decimal values. These data types are fundamental for performing mathematical operations and numerical analysis in data science.
# Examples of numeric data types
integer_num = 42
float_num = 3.14159
Strings (str) are used to represent text data. Text processing is a crucial part of data science, and Python's string manipulation capabilities make it a powerful tool for handling textual data.
# Examples of strings
name = "John Doe"
message = "Hello, Data Science!"
Lists (list) are versatile data structures that allow you to store collections of items. In data science, lists are frequently used to store datasets, sequences, or arrays of values. Lists can hold elements of different data types.
Tuples (tuple) are similar to lists but are immutable, meaning their elements cannot be modified once defined. They are often used to represent fixed collections of values.
# Example of a list
numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
# Example of a tuple
coordinates = (latitude, longitude)
Sets (set) are unordered collections of unique elements. They are valuable for tasks that require removing duplicate values or performing set operations like union, intersection, and difference.
Dictionaries (dict) are key-value pairs that allow you to store and retrieve data based on a unique key. They are excellent for organizing and accessing structured data, making them essential for tasks like data preprocessing.
# Example of a set
unique_numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
# Example of a dictionary
student = {"name": "Alice", "age": 25, "major": "Computer Science"}
Boolean data types (bool) represent truth values, typically denoted as True or False. They are essential for making decisions and controlling flow in data analysis and machine learning algorithms.
Python only accepts Boolean values that begin with a capital T or F. The boolean values true and false are incorrect, thus Python will throw an exception when they are used.
# Example of a boolean
print (type (True))
print (type (False))
Join our WhatsApp Channel to get the latest news, exclusives and videos on WhatsApp
_____________
Disclaimer: Analytics Insight does not provide financial advice or guidance. Also note that the cryptocurrencies mentioned/listed on the website could potentially be scams, i.e. designed to induce you to invest financial resources that may be lost forever and not be recoverable once investments are made. You are responsible for conducting your own research (DYOR) before making any investments. Read more here.
